First Aid & Emergency Equipment for Businesses.
Brands




Adapt the equipment to your industry
Restaurants & Food Industry
In kitchen environments, cuts and burn injuries are the most common. To comply with HACCP requirements, you must use blue detectable plasters that are visible if they end up in food.
Tip: Blue Plasters & Burn Gel
Industry & Workshop
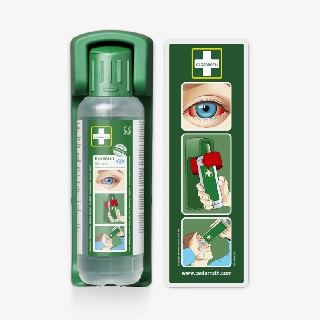
These environments require robust equipment that withstands dust and dirt. If chemicals are handled, a buffered eye wash is critical to protect eyesight in the event of an accident.
Tip: Eye Wash & Dust‑proof Cabinets
Office & Public Environments
Here, accessibility is key. A centrally located AED suitable for use by non‑professionals, along with simple plaster dispensers for everyday injuries.
Tip: AEDs & Wall‑mounted Dispensers
Important Information About Eye Injuries
In operations with a risk of splashes (e.g. cleaning services, laboratories and construction), time is critical. For chemical exposure, rinse immediately with a neutralising (buffered) solution. For dust, saline solution is often sufficient. Read more about eye wash here.
Do You Comply with Workplace Safety Regulations?
According to regulation AFS 1999:7, first aid equipment must be available and clearly marked. Make sure to label the equipment with our Emergency Signs and carry out an inventory check every six months.